
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
The latest diabetes news from News Medical |
|
|
|
|  | | | | | 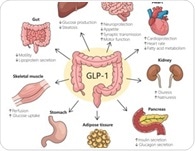 Can one drug do it all? Reviewing the expanding clinical universe of GLP-1 agonists Can one drug do it all? Reviewing the expanding clinical universe of GLP-1 agonists Landmark trials have shown that GLP-1 receptor agonists, originally developed for diabetes and weight loss, also provide significant benefits for cardiovascular, kidney, liver, joint, and sleep-related diseases. These effects extend beyond weight loss, suggesting anti-inflammatory mechanisms with broad potential for managing chronic diseases. | |  | | | | |  Heart healthy habits boost overall body health and longevity Heart healthy habits boost overall body health and longevity People who had more heart-healthy habits and factors, as assessed by the American Heart Association's Life's Simple 7 metrics for ideal cardiovascular health, had more positive benefits for whole body health, according to a review of research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open-access, peer-reviewed journal of the American Heart Association. | |  | | | | |  Nighttime avocado snack may support heart health in prediabetic adults Nighttime avocado snack may support heart health in prediabetic adults Findings from a newly published randomized controlled trial offer surprising insights for the one in three adults at greater risk of heart disease because of prediabetes. | |
|
|
|  | | |  Patients prescribed drugs to help them lose weight may experience a rebound in weight gain after halting their prescription, finds a meta-analysis published in BMC Medicine. Patients prescribed drugs to help them lose weight may experience a rebound in weight gain after halting their prescription, finds a meta-analysis published in BMC Medicine. | | | | |  Exposure to a class of synthetic chemicals known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)-often called "forever chemicals"-may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, according to a new study led by Mount Sinai researchers. Exposure to a class of synthetic chemicals known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)-often called "forever chemicals"-may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, according to a new study led by Mount Sinai researchers. | | | | |  Popular GLP-1 drugs help many people drop tremendous amounts of weight, but the drugs fail to provide a key improvement in heart and lung function essential for long-term good health, University of Virginia experts warn in a new paper. Popular GLP-1 drugs help many people drop tremendous amounts of weight, but the drugs fail to provide a key improvement in heart and lung function essential for long-term good health, University of Virginia experts warn in a new paper. | | | | |  An international team of researchers has made a key discovery: many children and young adults in Sub-Saharan Africa diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (T1D) may have a different form of the disease - one not caused by the immune system, unlike classic T1D. An international team of researchers has made a key discovery: many children and young adults in Sub-Saharan Africa diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (T1D) may have a different form of the disease - one not caused by the immune system, unlike classic T1D. | | | | |  Autosomal dominant optic atrophy (ADOA), the most common genetic optic neuropathy, is an insidious disease. It often presents slowly during childhood by way of blurry vision, trouble reading or focusing, and sometimes only as a failed vision test. Autosomal dominant optic atrophy (ADOA), the most common genetic optic neuropathy, is an insidious disease. It often presents slowly during childhood by way of blurry vision, trouble reading or focusing, and sometimes only as a failed vision test. | | | | |  Precancerous cells must adapt to and overcome cellular stress and inflammation in order to progress and form malignant tumors. Precancerous cells must adapt to and overcome cellular stress and inflammation in order to progress and form malignant tumors. | | | | |  A new review explains how fad diets and unregulated supplements promoted online can cause serious skin, hair, and nail problems, often before other symptoms appear. Clinicians are urged to recognize these risks and address health misinformation in the digital age. A new review explains how fad diets and unregulated supplements promoted online can cause serious skin, hair, and nail problems, often before other symptoms appear. Clinicians are urged to recognize these risks and address health misinformation in the digital age. | | | | |  The Stephenson Global Pancreatic Cancer Research Institute and its partner City of Hope, one of the country's largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations, today announced the six inaugural recipients of the prestigious Stephenson Scholar Grants, awarding $5.25 million to support high-impact research aimed at transforming the understanding, early detection and treatment of pancreatic cancer. The Stephenson Global Pancreatic Cancer Research Institute and its partner City of Hope, one of the country's largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations, today announced the six inaugural recipients of the prestigious Stephenson Scholar Grants, awarding $5.25 million to support high-impact research aimed at transforming the understanding, early detection and treatment of pancreatic cancer. | | | | |  Aging-related diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders and type 2 diabetes, are associated with defects in protein synthesis and folding. Aging-related diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders and type 2 diabetes, are associated with defects in protein synthesis and folding. | | | | |  Hispanic people have an increased risk of peripheral neuropathy compared to white people that cannot be explained by many health, lifestyle and social risk factors, according to a study published July 16, 2025, in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Hispanic people have an increased risk of peripheral neuropathy compared to white people that cannot be explained by many health, lifestyle and social risk factors, according to a study published July 16, 2025, in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. | | | | |  Diabetes affects millions worldwide, causing both nerve and metabolic complications. A recent study suggests that diabetic nerve damage may also lead to impaired bone health. Diabetes affects millions worldwide, causing both nerve and metabolic complications. A recent study suggests that diabetic nerve damage may also lead to impaired bone health. | | | | |  Many people with cancer experience dramatic loss of muscle and fat tissue. In many cases, even the heart muscle is affected, which further weakens the body. Many people with cancer experience dramatic loss of muscle and fat tissue. In many cases, even the heart muscle is affected, which further weakens the body. | | | | |  Extreme obesity in US youth has risen significantly, linked to higher rates of diabetes and liver complications, necessitating immediate public health action. Extreme obesity in US youth has risen significantly, linked to higher rates of diabetes and liver complications, necessitating immediate public health action. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|