
|
|
|
| |

|
|
| |
The latest men's health news from News Medical |
|
|
|
 | | |  Experts say you don’t need 10,000 steps, here’s the new magic number Experts say you don’t need 10,000 steps, here’s the new magic number A major systematic review finds that walking just 7,000 steps per day, rather than the traditional 10,000, can significantly reduce the risk of mortality, cardiovascular disease, dementia, and more. The analysis, published in The Lancet Public Health, provides an evidence-based and achievable target for adult health. | | | | |  Creatine may enhance neuroprotection through energy pathways Creatine may enhance neuroprotection through energy pathways Creatine supplementation may improve cognitive performance and mood, offering insights into its role in muscle-brain interactions and overall health. | |
|
|
| |  | | |  Gut fungal communities may impact multiple sclerosis severity, offering new insights into MS pathogenesis and potential microbiome-based treatment strategies. Gut fungal communities may impact multiple sclerosis severity, offering new insights into MS pathogenesis and potential microbiome-based treatment strategies. | | | | |  Older adults who consistently followed healthy dietary patterns, especially AHEI, MIND, and AMED, accumulated chronic diseases more slowly over 15 years. Diets high in pro-inflammatory foods were linked to a faster buildup of multimorbidity, particularly in cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric conditions. Older adults who consistently followed healthy dietary patterns, especially AHEI, MIND, and AMED, accumulated chronic diseases more slowly over 15 years. Diets high in pro-inflammatory foods were linked to a faster buildup of multimorbidity, particularly in cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric conditions. | | | | |  MRI findings indicate that smoking is linked to reduced brain volume, raising concerns about dementia risk, especially with higher body mass index. MRI findings indicate that smoking is linked to reduced brain volume, raising concerns about dementia risk, especially with higher body mass index. | | | | |  Long-term gluten reduction may disrupt gut microbiota balance, reducing beneficial bacteria and increasing ethanol, linked to inflammation and metabolic risks. Long-term gluten reduction may disrupt gut microbiota balance, reducing beneficial bacteria and increasing ethanol, linked to inflammation and metabolic risks. | | | | |  The CoVerage system monitors SARS-CoV-2 evolution, predicting variants and scoring amino acid changes to inform vaccine efficacy and public health strategies. The CoVerage system monitors SARS-CoV-2 evolution, predicting variants and scoring amino acid changes to inform vaccine efficacy and public health strategies. | | | | |  Investigating vegetable oils, this study reveals their effects on skin cell proliferation and migration, emphasizing the role of fatty acid composition. Investigating vegetable oils, this study reveals their effects on skin cell proliferation and migration, emphasizing the role of fatty acid composition. | | | | |  This study reveals how machine learning models uncover new genetic variants linked to Alzheimer’s, advancing predictive accuracy in genetic epidemiology. This study reveals how machine learning models uncover new genetic variants linked to Alzheimer’s, advancing predictive accuracy in genetic epidemiology. | | | | |  A major scoping review of recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses finds that most dairy products are either neutral or modestly protective for heart, cancer, metabolic, and mortality outcomes in adults. Yogurt and other fermented dairy consistently show the strongest health associations, while some risks remain for specific cancers. A major scoping review of recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses finds that most dairy products are either neutral or modestly protective for heart, cancer, metabolic, and mortality outcomes in adults. Yogurt and other fermented dairy consistently show the strongest health associations, while some risks remain for specific cancers. | | | | | 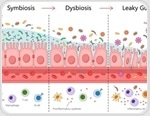 Researchers reviewed recent studies showing that gut dysbiosis contributes to heart failure by weakening the gut barrier, enabling harmful metabolites like TMAO to trigger inflammation and cardiac damage. The review highlights a bidirectional “gut-heart axis” and points to new avenues for dietary and microbial therapies. Researchers reviewed recent studies showing that gut dysbiosis contributes to heart failure by weakening the gut barrier, enabling harmful metabolites like TMAO to trigger inflammation and cardiac damage. The review highlights a bidirectional “gut-heart axis” and points to new avenues for dietary and microbial therapies. | | | | |  Congenital syphilis remains a critical issue in remote Australia, with healthcare barriers undermining effective STI screening and increasing pregnancy risks. Congenital syphilis remains a critical issue in remote Australia, with healthcare barriers undermining effective STI screening and increasing pregnancy risks. | | | | |  Boosting greenery may protect against air pollution's impact on dementia, revealing a potential strategy to reduce Alzheimer's disease burden globally. Boosting greenery may protect against air pollution's impact on dementia, revealing a potential strategy to reduce Alzheimer's disease burden globally. | | | | |  A nationwide Austrian study of nearly 9,000 teens reveals distinct health behaviors and motivations among vegetarian, vegan, and omnivorous students. Vegan and vegetarian youth are more likely to report higher fruit, vegetable, and activity levels, but still fall short of daily exercise targets. A nationwide Austrian study of nearly 9,000 teens reveals distinct health behaviors and motivations among vegetarian, vegan, and omnivorous students. Vegan and vegetarian youth are more likely to report higher fruit, vegetable, and activity levels, but still fall short of daily exercise targets. | | | | |  New research links ultra-processed food intake to increased diabetes risk in individuals with depression, highlighting the need for healthier dietary choices. New research links ultra-processed food intake to increased diabetes risk in individuals with depression, highlighting the need for healthier dietary choices. | | | | |  A new study in The Journal of Sexual Medicine found that participating in “No Nut November”, a month-long abstinence challenge, had no measurable effect on sexual well-being. The only significant difference was that participants reported higher sexual flexibility, likely reflecting a pre-existing trait. A new study in The Journal of Sexual Medicine found that participating in “No Nut November”, a month-long abstinence challenge, had no measurable effect on sexual well-being. The only significant difference was that participants reported higher sexual flexibility, likely reflecting a pre-existing trait. | | | | |  Analysis of UK self-tests reveals critical flaws in accuracy claims, highlighting risks and the need for enhanced regulatory standards for consumer safety. Analysis of UK self-tests reveals critical flaws in accuracy claims, highlighting risks and the need for enhanced regulatory standards for consumer safety. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|